In an Ecg Pattern the P Wave Is Caused by
The region between the QRS complex and T wave is referred to as the ST segment. All of the above.
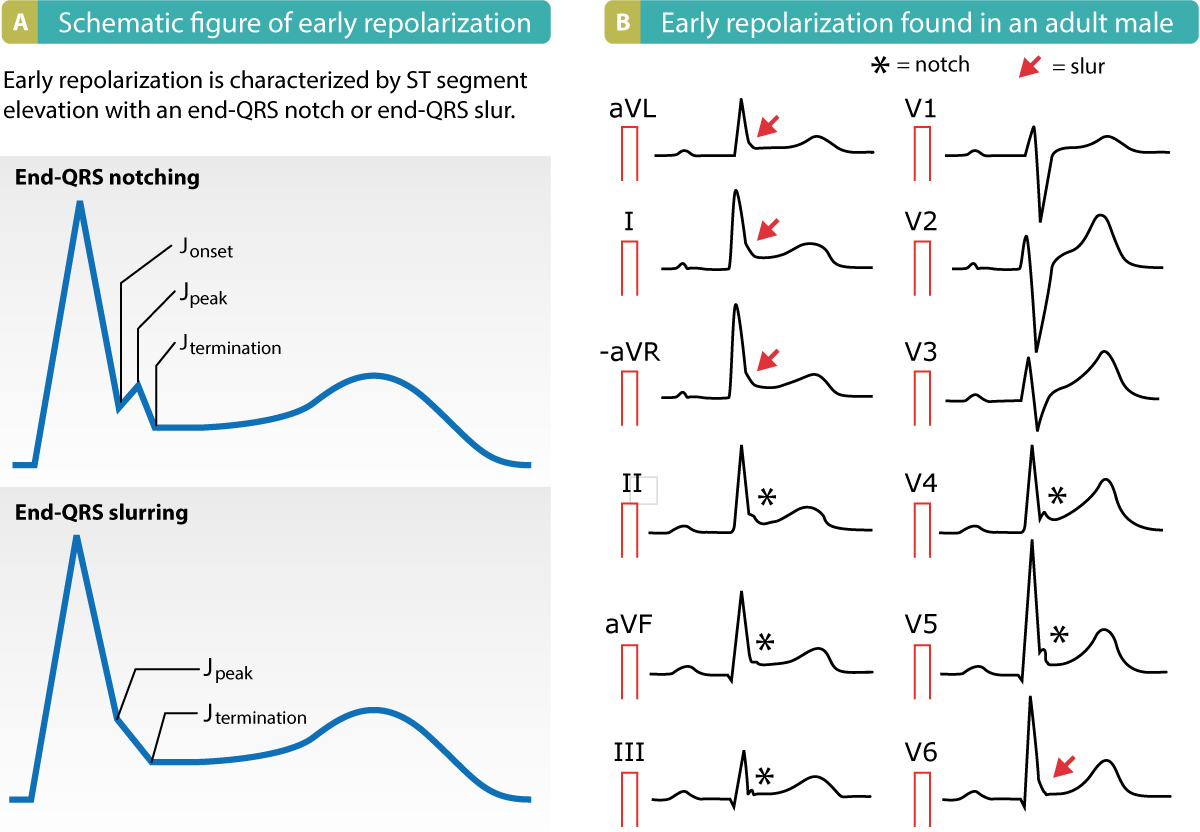
Early Repolarization Pattern On Ecg Early Repolarization Syndrome Ecg Echo
In an ECG pattern the P wave is caused by.
. This is an important clue to determine the presence of a lead reversal. When the P wave moves rock particles move back and forth along. The _____ is referred to as the pacemaker of the heart.
Depolarization of ventricular muscle fibers. Absence of P Waves. The right and left atrial waveforms summate to form the P wave.
The PR interval is assessed in order to determine whether impulse conduction from the atria to the ventricles. Depolarization of atrial muscle fibers. B repolarization of ventricular muscle fibers.
They represent the depolarization of both the right and left atria which occur at the same time. It is typically a small positive deflection from the isoelectric baseline that occurs just before the QRS complex. Depolarization of atrial muscle fibers.
LALL reversal has the tential to create a pseudoinferior wall infarct pattern on the ECG. A lack of visible P waves preceding QRS complexes suggests a lack of sinus beats. Ng to anothe qdestio estion 1 In an ECG pattern the P wave is caused by O A.
Question 3 The right atrium receives blood directly from the. Factors that increase the heart rate and blood pressure include. The P wave may also be hidden within the QRS complex.
In most leads eg. Which of the following is the most life threatening. In a ECG pattern the T wave is caused by.
In an ECG pattern the T wave is caused due to repolarisation of ventricular msucle fibres and P wave is caused due View the full answer Transcribed image text. Asked Jun 14 2016 in Anatomy Physiology by Heartfelt. The region between the P wave and QRS complex is known as the PR segment.
She notices that while her features are similar to her parents features. Polarization of atrial muscle fibers. The P-wave PR interval and PR segment.
Mar 08 2022 0608 AM. Question 4 The pain associated with the condition called angina pectoris usually is caused by an obstruction in an artery that. Polarization of ventricular muscle fibers.
If the first component of the P wave in lead II is greater than 25 mm in height we think of right atrial enlargementIt could also just be nothing or could signify a mild abnormality in where the atrial activation is coming from. A Repolarization of the ventricular muscle fibers. P waves are the first waveform in the complete complex normally found upright in most leads.
Therefore knowing deadly ECG patterns. The segment between the P wave and the R wave represents the delay of the electrical circuit in the AV node. The middle 13 is a combination of the two.
This may occur with sinus dysfunction or in the presence of fibrillation or flutter waves. - 19464922 021113 31 32 33 Kai looks at a photo of herself with her parents. In an EKG or EEG pattern the P wave is caused by.
The P-wave reflects atrial depolarization activation. C depolarization of atrial muscle fibers. The PR interval is the distance between the onset of the P-wave to the onset of the QRS complex.
P waves are the first seismic waves felt during an earthquake. The first 13 of the P wave corresponds to right atrial activation the final 13 corresponds to left atrial activation. The radial and ulner veins merge to form the___vein.
The _____ rhythmically forms impulses initiating each heartbeat and transmits these inpulses to the _____. Changes need to occur in at least 2 of the right precordial leads V1-3. A depolarization of ventricular muscle fibers.
The region between 2 waves is called a segment. Depends on the lead. Polarization of atrial muscle fibers в.
Answer- The first depletion is the P wave. Depolarization of atrial muscle fibers. It can sometimes have abnormalities in morphology or timing that can be indicative of significant.
Type 1 Coved ST elevation 2mm at the J-point followed by an inverted T wave. The P wave is a small wave in relationship to other waves on the ECG paper. The P wave is a summation wave electrical activity that comes from successive signaling from multiple points causing wave-like contractions.
The P wave QRS complex and T wave are the parts of an EKG in which there are changes in voltage waves. D repolarization of atrial muscle fibers. The P wave and PR segment is an integral part of an electrocardiogram ECG.
Lead II the right and left atrial waveforms move in the same direction forming a monophasic P. An average ER physician performs around 100 tasks in an hour and gets interrupted at least every 6 minutes. In an ECG pattern the P wave is caused by.
In an ECG pattern the P wave is caused by. One of the common interruptions in the ED is a request to sign off on an ECG of a patient who has been triaged but not seen by a doctor yet. Deadly ECG Patterns 5 Cant Miss ECG Findings.
A P wave on an electrocardiogram represents a phase of electrical activity that causes the atria of the heart to contract. It represents the electrical depolarization of the atria of the heart. ECG interpretation traditionally starts with an assessment of the P-wave.
Question 42 In an ECG pattern the P wave is caused by. Question 2 Cells of the conducting system in the heart are more sensitive to which ion. View the full answer.
Depolarization of atrial muscle fibers depolarization of ventricular muscle fibers A. There are three ECG patterns associated with Brugada syndrome of which only the type 1 ECG is diagnostic. Polarization of ventricular muscle fibers Ос.
LALL reversal also causes inverted P waves in III. This totally depends on the lead of the ECG you are looking at and which part of the P wave is pointed. That is because aThe atria are not as muscular as the ventricles and so require less electrical stimulation to cause contra.
A P wave is a type of seismic wave that is caused by an earthquake. In an ECG pattern the P wave is caused by.

Pin By Tonya On Medic 12 Lead Cardiology Study Medical Mnemonics Study Cards

Three Different Ecg Patterns In Right Precordial Leads Frequently Download Scientific Diagram

Rad Due To Rvh Axis Example 002 Interpretation Estimate Analysis

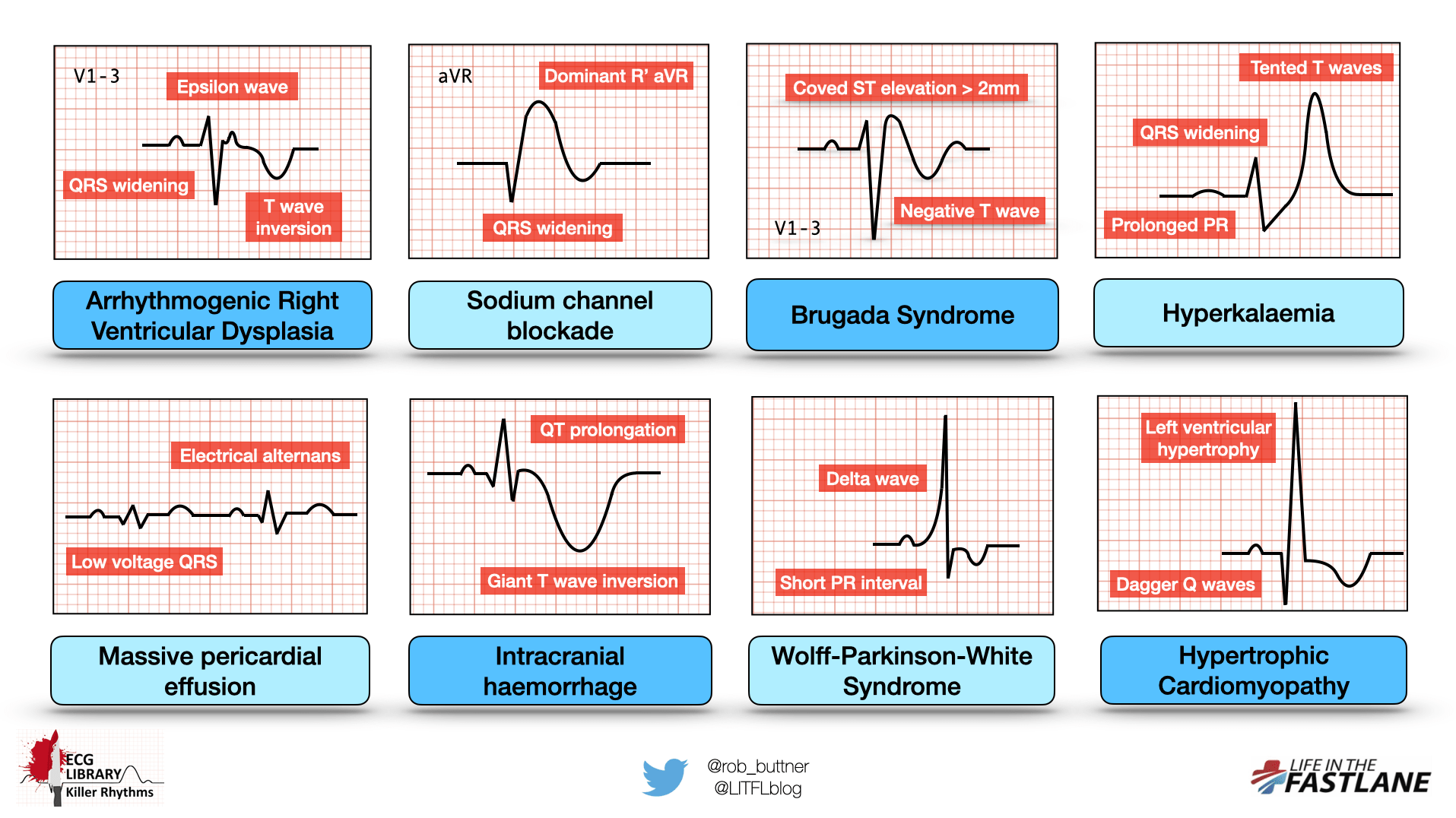
Killer Ecg Patterns Part 1 Litfl Ecg Library

Pin On Cardiology Related Fields

The Ecg Patterns Of The Preinfarction Syndrome And Evolving Myocardial Download Scientific Diagram

Schematic Representations Of Ecg Patterns Normal Ecg Pattern With Download Scientific Diagram

Typical Ecg Pattern In A Case Of Lqt1 3 A Broad Based T Wave Is Download Scientific Diagram

Three Different Ecg Patterns In Right Precordial Leads Frequently Download Scientific Diagram

Lead Ii Ecg Trace Pattern Of A Normal Rat Showing Regular Ecg Download Scientific Diagram

Pin By Jason Winter Ecg Educator On Ecg Ekg Green Memo Cards Ekg Cardiology Memo
Killer Ecg Patterns Part 1 Litfl Ecg Library

Figure 3 Characteristic T Wave Inversions Caused By Wellen S Syndrome Th Medical School Motivation Acute Coronary Syndrome Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
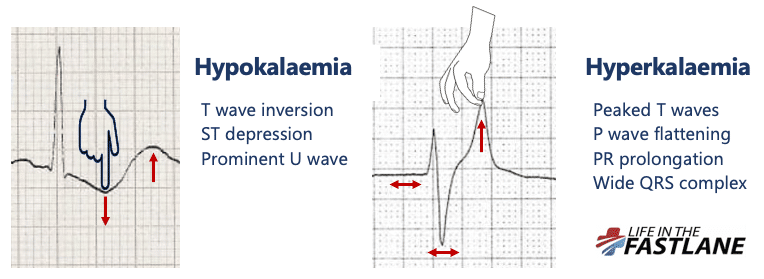
Ecg Interpretation Characteristics Of The Normal Ecg P Wave Qrs Complex St Segment T Wave Ecg Echo

St Segment Elevation In Acute Myocardial Ischemia And Differential Diagnoses Ecg Learning Segmentation Brugada Syndrome Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy




Comments
Post a Comment